While cardio provides numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular function, weight loss, and stress reduction, achieving desired results through exercise alone can be challenging. Proper diet management is essential.
Food consumed before and after exercise directly impacts stamina, recovery speed, and weight loss effectiveness. This article will explore the necessary nutrients, recommended diets, and specific tips for maximizing the effects of cardio.

Pre and Post Workout Diet
Importance of Pre-Workout Nutrition
Why Pre-Workout Nutrition Matters
Food consumed before exercise provides energy, prevents muscle damage during exercise, and prevents fatigue.
Carbohydrates are the primary energy source used during exercise; deficiency can lead to fatigue and decreased performance. A small amount of protein is also beneficial in reducing muscle damage and aiding recovery.
Timing of Pre-Workout Intake
- 1-3 hours before exercise: Finish a moderate-sized meal to allow for sufficient digestion.
- 30 minutes to 1 hour before exercise: If short on time, choose easily digestible, light snacks.
Recommended Pre-Workout Diet
1. Simple carbohydrate-focused meal
- Banana: Rich in natural sugars and potassium, providing immediate energy and preventing muscle cramps.
- Whole-wheat toast: Complex carbohydrates release energy slowly, suitable for prolonged exercise.
- Oatmeal (low-fiber): Easily digestible and provides sustained energy.
2. Adding a small amount of protein
- Greek yogurt with honey: Combines protein with quickly absorbed sugars.
- Boiled egg: Convenient and provides high-quality protein.
- Drink plenty of water before exercise to prevent dehydration, a major cause of fatigue and reduced performance.
Foods to Avoid Before Exercise
- High-fat foods: Slow digestion can burden the stomach.
- High-fiber foods: Can cause bloating.
Importance of Post-Workout Nutrition
Why Post-Workout Nutrition Matters
Post-workout meals are essential for replenishing spent energy and aiding muscle recovery. The 30-minute to 2-hour period after exercise is the "golden time" for optimal nutrient absorption, reducing fatigue and accelerating recovery.
Post-workout intake timing: Replenish energy within 30 minutes of finishing your workout. Nutrient absorption is highest during this time, making it effective for recovery and muscle regeneration.
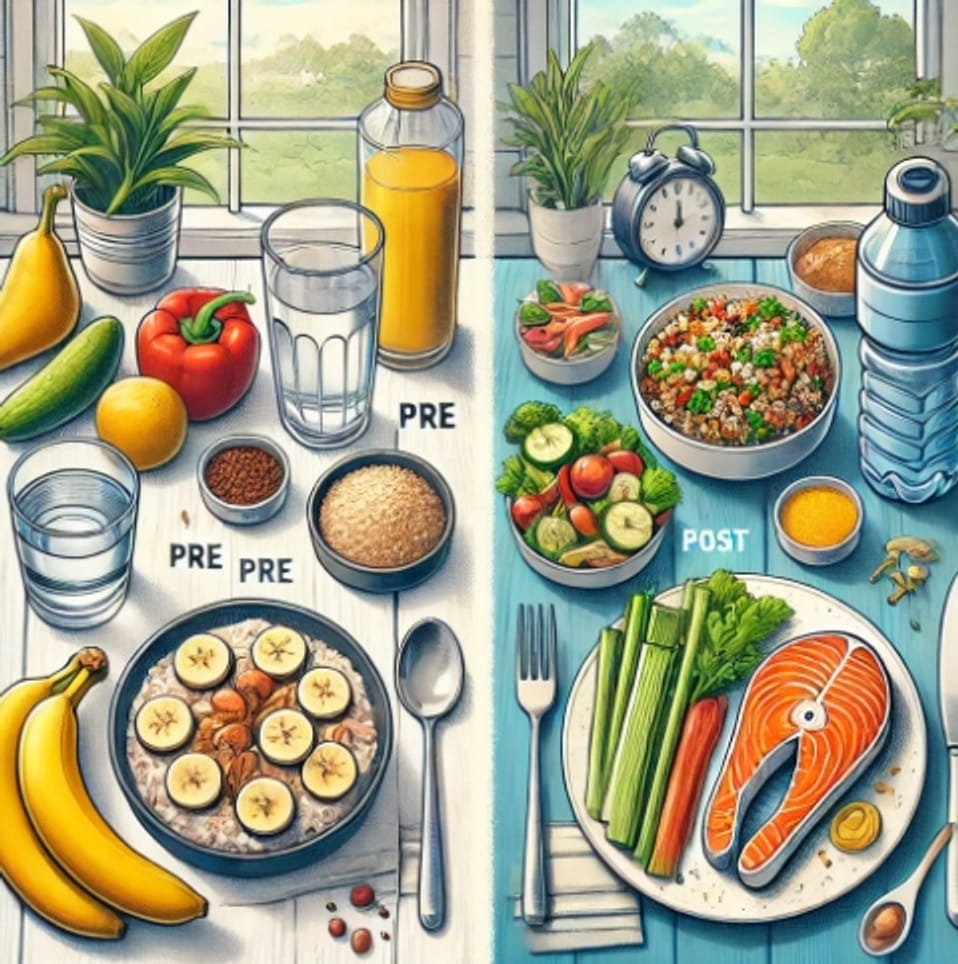
Pre and Post Workout Diet Comparison
Recommended Post-Workout Diet: A balance of carbohydrates and protein
- Carbohydrates: Necessary to replenish depleted glycogen.
- Whole-wheat toast + avocado + boiled egg
- Banana + Greek yogurt + berry smoothie
- Protein: Repairs and regenerates muscle damage. Choose high-protein foods like chicken breast, fish, or tofu.
- Healthy fats: Almonds, walnuts, and avocados reduce inflammation and aid recovery. Consume in moderation to enhance energy replenishment.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to replenish fluids and electrolytes lost through sweat. Sports drinks are also suitable after high-intensity workouts.
Foods to Avoid After Exercise
- High-sugar snacks: Can cause a blood sugar spike followed by a sharp drop.
- Excessive caffeine: Can lead to dehydration, so be cautious.
Overall Dietary Strategies for Cardio
Adjusting Your Diet Based on Exercise Intensity
- High-intensity workouts: Require more carbohydrates and protein. Utilize quickly absorbed foods like smoothies and protein shakes.
- Low-intensity workouts: Smaller amounts of carbohydrates are sufficient. Consume simple snacks like bananas or nuts.
Adjusting Your Diet Based on Workout Time
- Before morning workouts: Consume easily digestible carbohydrates like bananas or oatmeal.
- After evening workouts: Choose a light, protein-focused meal like chicken breast or tofu, and avoid overeating.
Common Tips for Before and After Exercise
- Eat small, frequent meals: Avoid overeating and focus on easily digestible foods.
- Maintain balanced nutrition: Prepare meals with a proper balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fats.
- Choose foods that suit your body type: If certain foods cause digestive discomfort, try alternative foods.
- Prepare your meals in advance: Preparing snacks before and after exercise can make it easier to stick to your workout routine (e.g., nuts, bananas, protein shakes).
Additional Tips Related to Cardio Diets
Keep a workout log: Recording workout times, intensity, and diet can help you find the optimal routine for your body.
Use nutritional supplements: Protein powder, BCAAs, etc., can be used as needed, but avoid overconsumption.
Manage your diet with a friend: Planning your diet and exercising together can strengthen motivation.
To maximize the effectiveness of cardio, managing your diet before and after exercise is crucial. You need to supply sufficient energy before exercise and replenish the spent energy and aid muscle recovery afterwards.
Maintaining a balance of carbohydrates and protein, and consistently following a diet tailored to your body type and fitness goals, will lead to healthy and efficient results.

Comments0